

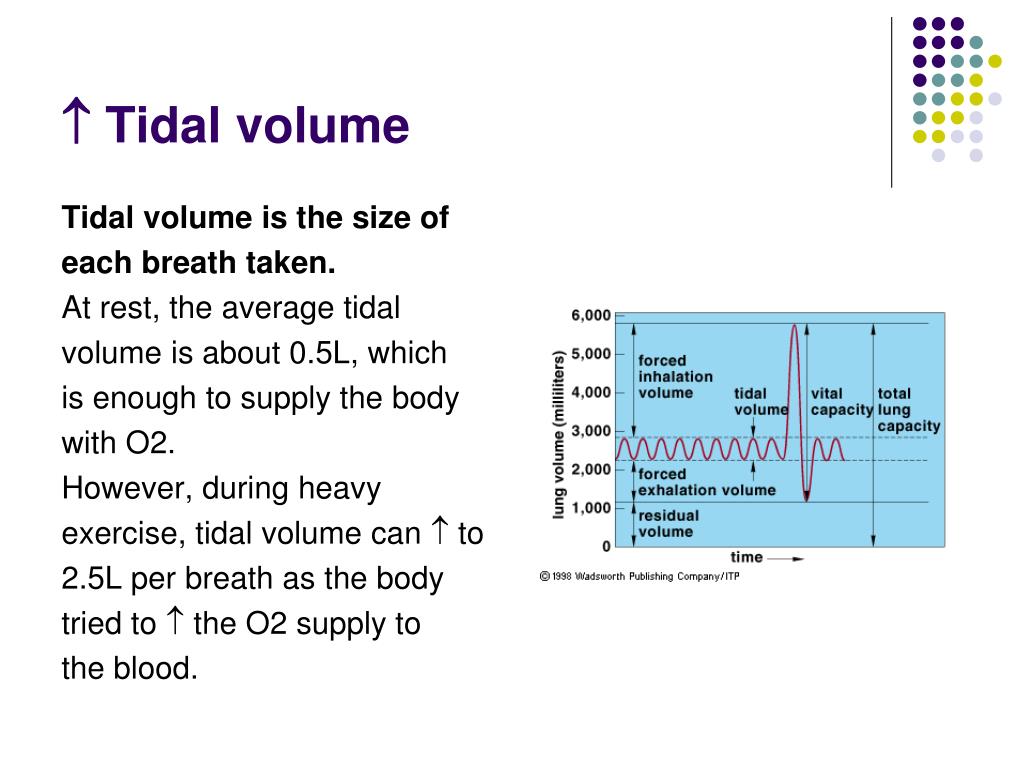
On Butterfly Ward this is usually un-cuffed Endotracheal Tube (ETT): An airway catheter inserted into the trachea (windpipe) via the mouth or nose in endotracheal intubation.The aim of the guideline is to outline the principles of management for infants requiring ETT suction for clinicians on Butterfly Ward at the Royal Children’s Hospital. The goal of ETT suction should be to maximise the amount of secretions removed with minimal adverse effects associated with the procedure. The safe range of ventilation for this patient is 315-420ml and the respective tidal volumes for 6, 7, and 8 ml/kg are 315, 365 and 420 ml respectively.Endotracheal intubation prevents the cough reflex and interferes with normal muco-ciliary function, therefore increasing airway secretion production and decreasing the ability to clear secretions.Įndotracheal tube (ETT) suction is necessary to clear secretions and to maintain airway patency, and to therefore optimise oxygenation and ventilation in a ventilated patient.ĮTT suction is a common procedure carried out on intubated infants. Therefore, the safe range of ventilation is 490-660ml (6-8ml/kg) and the respective tidal volumes for 6,7,8 ml/kg are 490, 575 and 660 ml respectively.
Tidal volume of 8ml/kg = 82.2 kg x 8 ml/kg Tidal volume of 7ml/kg = 82.2 kg x 7 ml/kg Tidal volume of 6ml/kg = 82.2 kg x 6 ml/kg Remember, the safe range for tidal volumes is 6-8 ml/kg.
#Vent tidal volume chart how to
We have already learned how to calculate IBW (steps 1 and 2), so let’s try step 3 using the IBWs that were calculated earlier in this chapter. Note: you will always round your result up or down to match the settings on the ventilator (usually, they use whole numbers only and count by 5s).
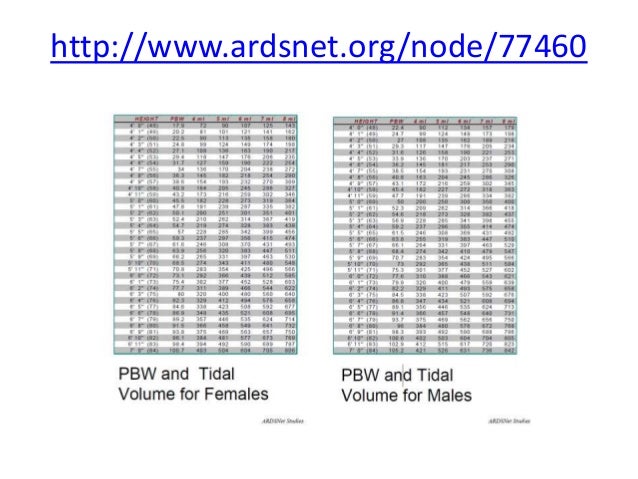
This approach still resulted in volutrauma and VILI. Even with the determination of using the ideal body weight instead of actual body weight, historically, tidal volumes of 10 ml for every kilogram of IBW were often used.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
